Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Mahdavi, M. A.*; Baker, D. R.*
Physics of Plasmas, 8(5), p.1607 - 1611, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ueta, Shinzo*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-069, 41 Pages, 1999/11
As a part of the evaluation for the sorption phenomena of nuclides in compacted bentonite, apparent diffusivities for uranium, neptunium and technetium that are redox-sensitive elements, were measured under reducing conditions. Bentonite used was a sodium bentonite, Kunigel V1. Apparent diffusivities were measured by using in-diffusion method (concentration profile method), under the conditions with varying dry densities of compacted bentonite and sorts of the solution used for water saturation of bentonite in diffusion experiments. As a result of the measurements, following ranges of values for apparent diffusivities were acquired. ...
Sugita, Yutaka; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Fujita, Tomoo; Tranduc, P.*
JNC TN8430 99-009, 45 Pages, 1999/06
It is an important part of the near field performance assessment of nuclear waste disposal to evaluate coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical (T-H-M) phenomena, e.g., thermal effects on groundwater flow through rock matrix and water seepage into the buffer material, the generation of swelling pressure of the buffer material, and thermal stresses potentially affecting porosity and fracture apertures of the rock. An in-situ T-H-M experiment named "Engineered Barrier Experiment" was conducted at the Kamaishi Mine, in which the host rock is granodiorite, in order to establish conceptual models of the coupled T-H-M processes and to build confidence in mathematical models and computer codes. This report summarizes the results of the in-situ direct compaction technique to evaluate the appropriate conditions for this technique. The in-situ direct compaction technique is one of the major candidate emplacement techniques for the buffer material. This experiment consisted of the mock-up tests and the in-situ test. The mock-up tests showed the appropriate conditions for the in-situ direct compaction technique. For the in-situ experiment, the manufactured OT-9607 achieved dry density averaged 1.65 g/cm , which matched the demand for the thermo-hydro-mechanical experiment.
, which matched the demand for the thermo-hydro-mechanical experiment.
; ; Sato, Haruo; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-088, 58 Pages, 1999/06
Sorption and diffusion behavior of palladium, which has been identified as one of the hazardous radionuclides in performance assessment of HLW disposal, in bentonite, granodiorite and tuff was studied in order to make reliable data set for the performance assessment. Sorption experiments of Pd on bentonite, granodiorite and tuff were conducted as functions of pH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio by batch method under aerobic conditions at room temperature. The distribution coefficients (K ) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10
) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /kg and were in the order of bentonite
/kg and were in the order of bentonite  granodiorite
granodiorite  tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K
tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K
values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K was not found in a range of 10
was not found in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 , but K
, but K values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K
values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m
was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m /kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH)
/kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH) (aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K
(aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K
values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH
values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO
type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO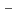 sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D
sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
PATRICIA F SALTE*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Apted, M. J.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-023, 231 Pages, 1999/05
The groundwater chemistry is one of important geological environment for performance assessment of high level radioactive disposal system. This report describes the results of geostatistical analysis of groundwater chemistry in Japan. Over 15,000 separate groundwater analyses have been collected of deep Japanese groundwaters for the purpose of evaluating the range of geochemical conditions for geological radioactive waste repositories in Japan. The significance to issues such as radioelement solubility limits, sorption, corrosion of overpack, behavior of compacted clay buffers, and many other factors involved in safety assessment. It is important therefore, that a small, but representative set of groundwater types be identified so that defensible models and data for generic repository performance assessment can be established. Principal component analysis (PCA) is used to categorize representative deep groundwater types from this extensive data set. PCA is a multi-variate statistical analysis technique, similar to factor analysis or eigenvector analysis, designed to provide the best possible resolution of the variability within multi-variate data sets. PCA allows the graphical inspection of the most important similarities (clustering) and differences among samples, based on simultaneous consideration of all variables in the dataset, in a low dimensionality plot. It also allows the analyst to determine the reasons behind any pattern that is observed. In this study, PCA has been aided by hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), in which statistical indices of similarity among multiple samples are used to distinguish distinct clusters of samples. HCA allows the natural, a priori, grouping of data into clusters showing similar attributes and is graphically represented in a dendrogram Pirouette is the multivariate statistical software package used to conduct the PCA and HCA for the Japanese groundwater dataset. An audit of the initial 15,000 sample dataset on the ...
Moribayashi, Kengo*; Sasaki, Akira; Tajima, Toshiki*
Physical Review A, 59(4), p.2732 - 2737, 1999/04
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:78.57(Optics)no abstracts in English
; ;
PNC TN9410 98-014, 46 Pages, 1997/11
Thermal conductivity of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel for fast reactor at beginning-of-life was correlated based on the recent results in order to apply to the fuel design and the fuel performance analysis. A number of experimental results of unirradiated fuel speimens were corrected from open literatures and PNC internal reports and examined for the database. Thermal conductivity of acutual fuel with porosity ( ), that of fully dense fuel (
), that of fully dense fuel ( 100%TD) and porosity correction factor (F) had theoretically the following correlation :
100%TD) and porosity correction factor (F) had theoretically the following correlation :  = F
= F 100%TD. The following correlation was developed for fully dense fuel by the results of high density fuel pellets which the effect of porosity was relatively small. The data base ranged from 17 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, from 1.90 to 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 90 to 98% of theoretical density and from 400 to 2090 degree C for temperature.
100%TD. The following correlation was developed for fully dense fuel by the results of high density fuel pellets which the effect of porosity was relatively small. The data base ranged from 17 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, from 1.90 to 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 90 to 98% of theoretical density and from 400 to 2090 degree C for temperature. 
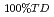 = (1/(-0.03237+0.8606
= (1/(-0.03237+0.8606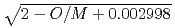 +2.483
+2.483 10
10 T))+75.27
T))+75.27 10
10 T
T where
where  100%TD: Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) T: Temperature (K) O/Z: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-) In this work two porosity correction factors were needed for high density fuel and low density fuel (around the current Monju specification). For high density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density :
100%TD: Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) T: Temperature (K) O/Z: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-) In this work two porosity correction factors were needed for high density fuel and low density fuel (around the current Monju specification). For high density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density :  90%TD) F
90%TD) F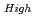 = 1-2.95P(P:Porosity volume Fraction (-)) For low density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density: around 85%TD) F
= 1-2.95P(P:Porosity volume Fraction (-)) For low density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density: around 85%TD) F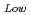 = 1-1.4P (P: Porosity volume Fraction (-)) The universal porosity correction factor was not determined in this work. In the next step, theoretical and analytical considerations should be taken into account.
= 1-1.4P (P: Porosity volume Fraction (-)) The universal porosity correction factor was not determined in this work. In the next step, theoretical and analytical considerations should be taken into account.
Fukuda, Takeshi; Sato, Masayasu; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; JT-60 Team
Fusion Energy 1996, Vol.1, p.857 - 866, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Takeshi; Takizuka, Tomonori; ; Kamada, Yutaka; Nagashima, Keisuke; Sato, Masayasu; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ishida, Shinichi; Konoshima, Shigeru; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 37(9), p.1199 - 1213, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:74.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English